Public-Private Partnership (PPP) is an effective tool that can contribute to enhancing economic and social development in Libya. After years of conflict and instability, the country needs innovative strategies to attract investment and improve infrastructure and public services. This article aims to explore the concept of PPP, its benefits, and the challenges facing its implementation in the Libyan context.
Public-Private Partnership (PPP) is an effective tool that can contribute to enhancing economic and social development in Libya. After years of conflict and instability, the country needs innovative strategies to attract investment and improve infrastructure and public services. This article aims to explore the concept of PPP, its benefits, and the challenges facing its implementation in the Libyan context.
Definition of PPP
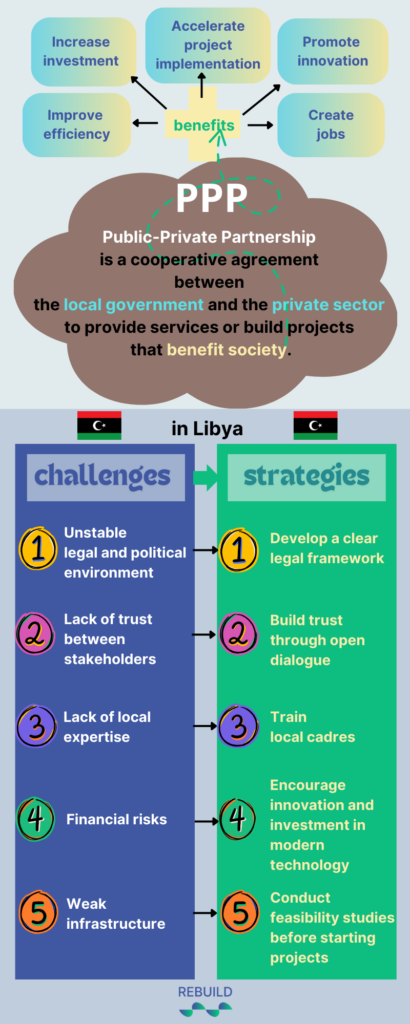
Public-Private Partnership is a cooperative agreement between the government and the private sector to provide services or build projects that benefit society. These partnerships typically involve sharing risks and rewards, with each party contributing its resources and expertise to achieve common goals.
Benefits of PPP
- Improved efficiency: The private sector has significant experience in managing projects and delivering services more efficiently than the public sector. This can lead to improved service quality and reduced costs.
- Increased investment: By attracting private sector investors, the government can obtain the necessary financing for infrastructure projects without having to burden its budget with additional burdens.
- Accelerating project implementation: Private companies have the ability to implement projects more quickly due to their flexibility and available resources.
- Promoting innovation: Collaboration with the private sector encourages the introduction of new technologies and innovative ideas to improve public services.
- Creating jobs: Partnership projects contribute to creating new jobs and strengthening the local economy.
Challenges facing PPPs in Libya
Despite the many benefits, PPPs in Libya face several challenges:
- Unstable legal and political environment: The lack of a clear legal framework regulating partnerships may hinder investment and increase business risks.
- Lack of trust between stakeholders: A history of conflict and strife has led to a loss of trust between the government and the private sector, making cooperation difficult.
- Lack of local expertise: Local institutions may lack the expertise needed to manage effective partnerships with large companies.
- Financial risks: There may be concerns about the government’s ability to meet its financial obligations, which negatively affects investors’ willingness to enter into long-term partnerships.
- Weak infrastructure: Libya needs to improve its basic infrastructure to make it an attractive environment for investment.
Strategies to enhance public-private partnerships
To overcome these challenges and enhance the effectiveness of partnerships, several steps can be taken:
- Develop a clear legal framework: The government must establish clear laws that regulate partnership operations and define the rights and obligations of each party.
- Build trust through open dialogue: Organize workshops and conferences that bring together government and private sector representatives to enhance communication and build mutual trust.
- Train local cadres: Provide training programs to qualify local cadres to manage partnership projects effectively.
- Encourage innovation and investment in modern technology: Support innovations that can improve the efficiency of services provided through these partnerships.
- Conduct comprehensive feasibility studies before starting projects: To ensure that projects are viable and profitable for all parties involved.
Conclusion
Enhancing public-private partnerships is a vital step towards achieving sustainable development in Libya. Despite the existing challenges, the available opportunities make it necessary to exploit this model to achieve the desired development goals and improve the standard of living of Libyan citizens.
 —
—
SEE ALSO
Public Finance Management in Municipalities
Necessary Skills in Procurement Planning for Libyan Municipalities
—